
|
||
Parallel Regions Soil Model in MALZThe Parallel Regions soil model, where the effects of Boundaries between Regions are explicitly modelled using currents on the discretized boundaries, is still relatively recent: it was introduced in V18.0 and it featured an improved tiling algorithm and a new UI in V19.0. Users could then graphically specify a point on one boundary and the thicknesses of regions between parallel boundaries to define the model. 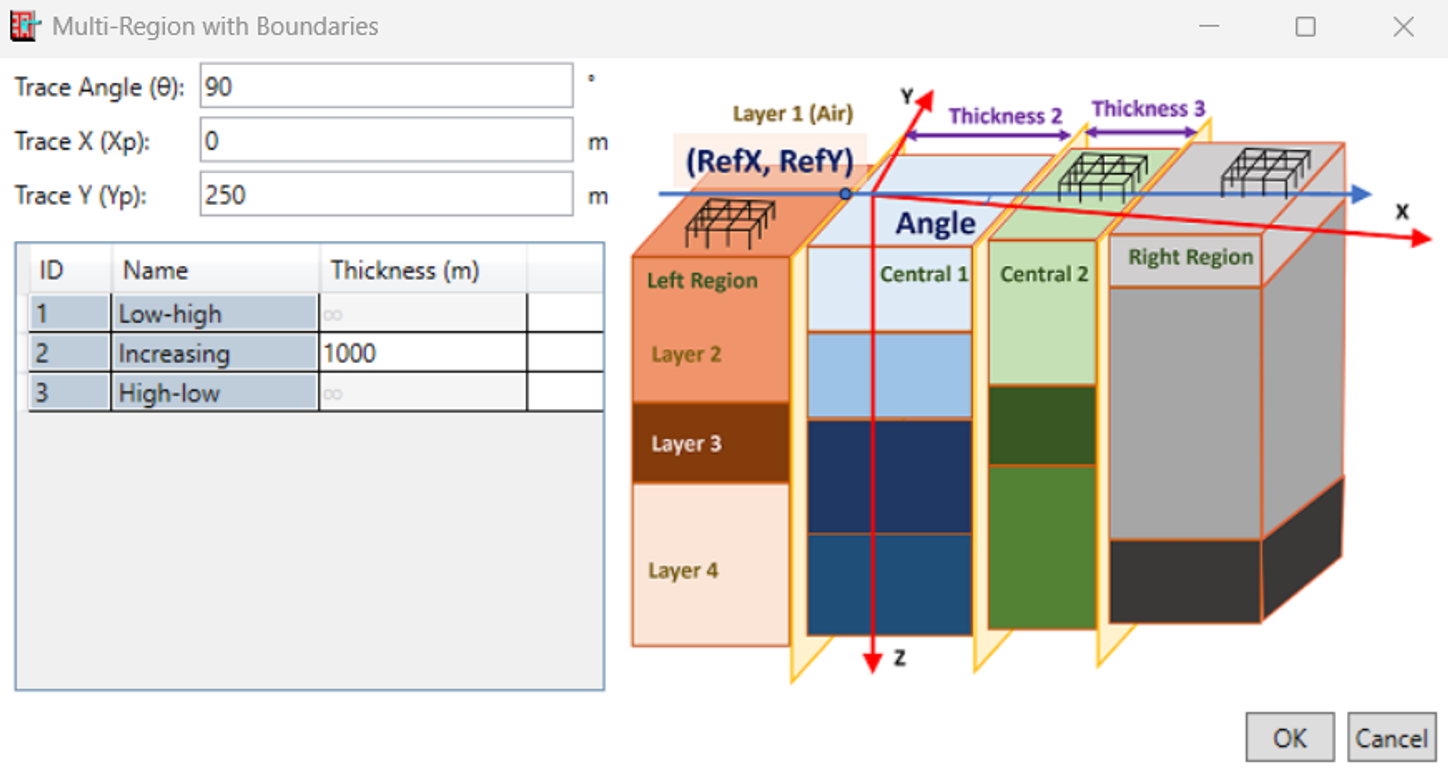
Next we discuss its usage: when results will be the same as those of the Multi-Region soil model, where conductors are assigned to soil regions as chosen by the user and which uses an approximation where boundaries are ignored, and when they could be different. 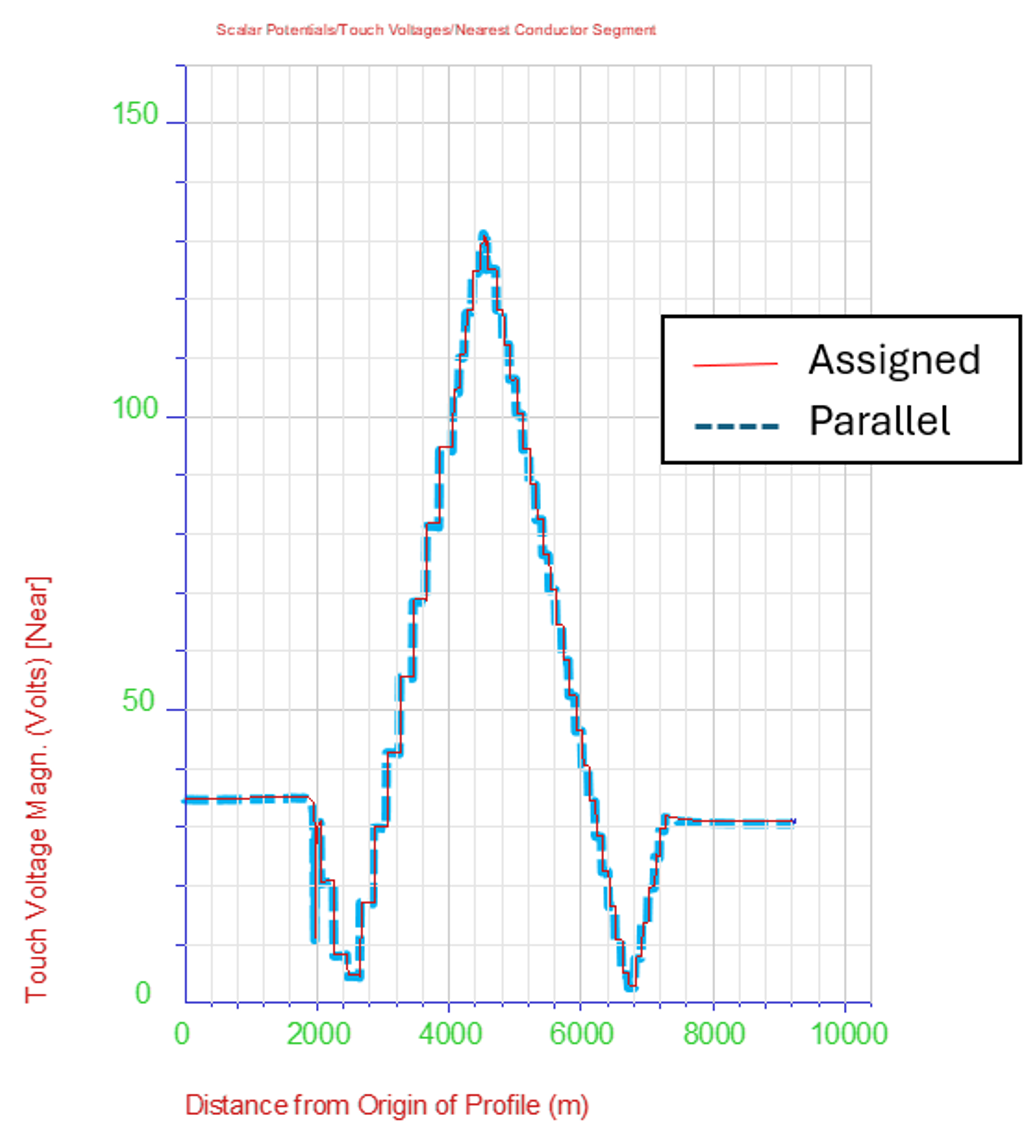
for the Multi-Region (User Assigned) and the Parallel Regions soil models. As the image above illustrates with a touch voltage plot on a pipeline, for standard right-of-way situations where the pipeline is well coated, the two models give the same results and there is no need for using the Parallel Regions soil model, which is more computationally demanding. 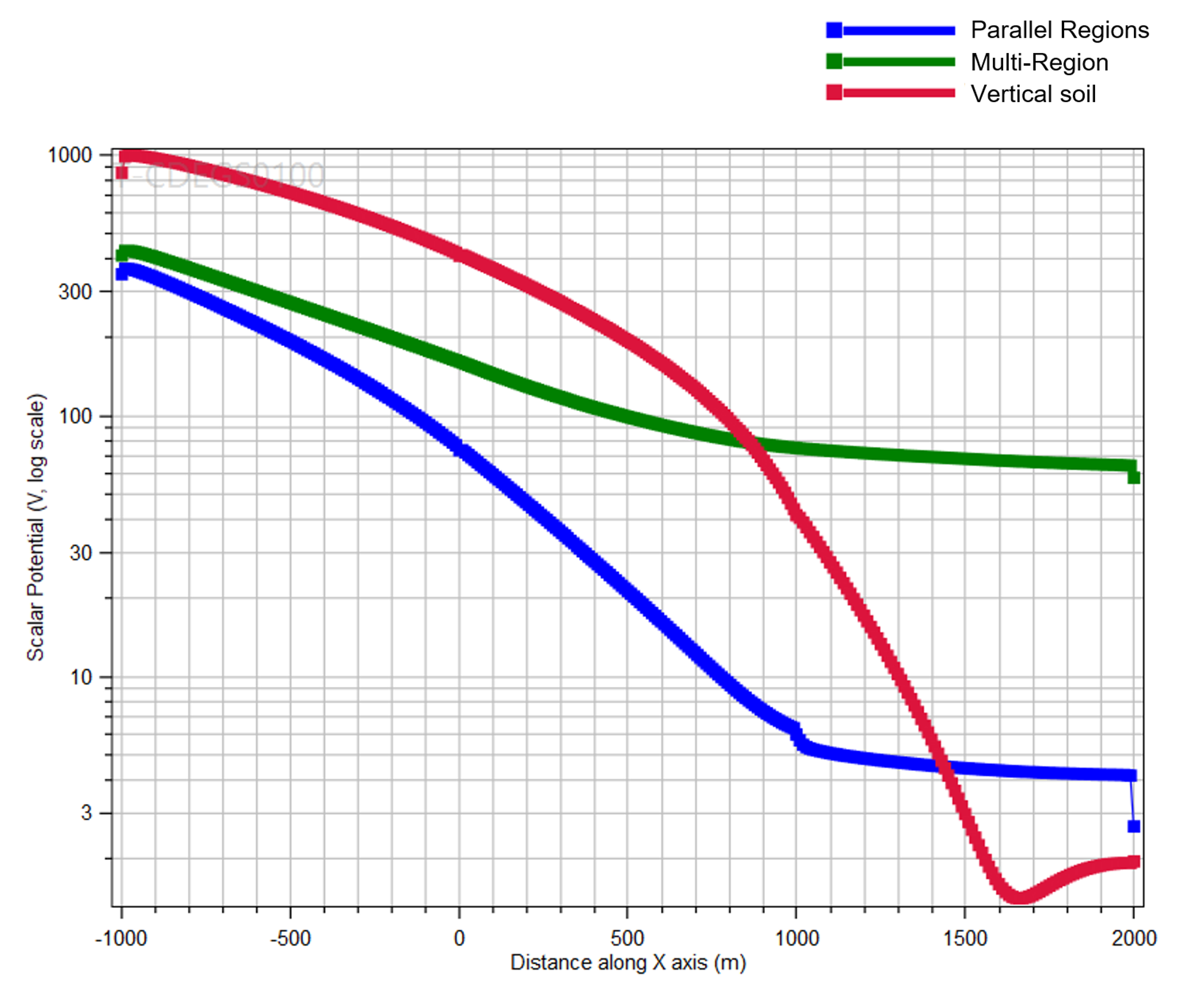
After building the models, the strategies for validating the results include using a simpler and computationally faster uniform soil model to calibrate the discretization of the boundaries and visualizing the discretization pattern and the currents on the boundaries.
|
||
|